Networking Requirements for Pixera
- Network Switch must be Multicast capable
- Speed must be at least 1Gbps
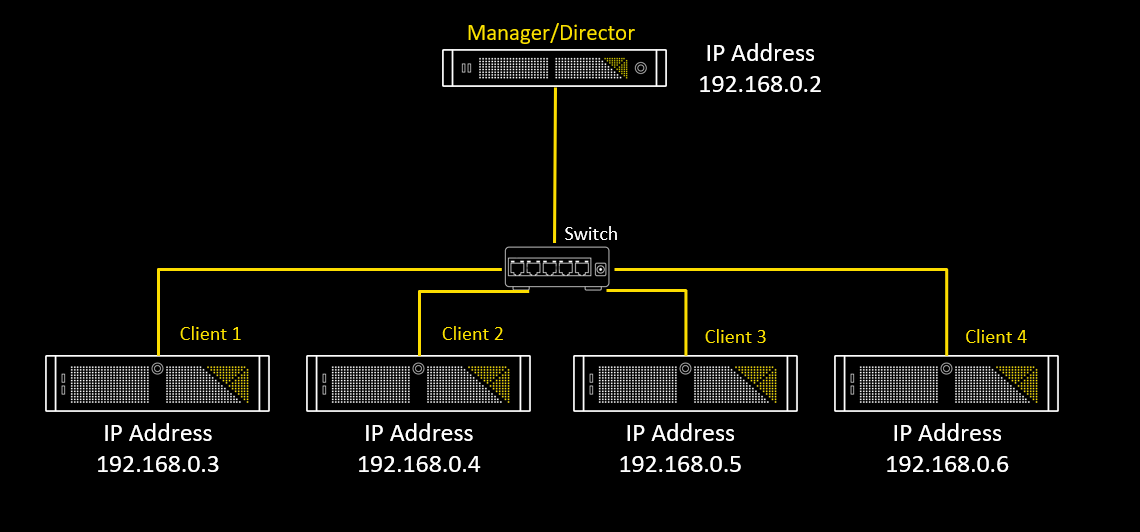
- Director and Clients must be in the same IP range
- It's recommended to turn off Firewalls on any servers!
- It's recommended not to use a USB to network adapter!
- It's recommended that the PIXERA Discovery network, and Presence Adapter IP, are not the same network as the internet
IPv4
IP (Internet Protocol) addresses are how we give devices on a network a unique identifier (sort of like a postal address).
We can set a Static IP address (recommended) or an address can be Dynamic. Static IP addresses are set in the Network and Sharing Center in Windows. Dynamic IP Addresses are set by a DHCP server on the networking and are generally not recommended as it's possible for a server to receive a different IP address on a restart which can have a ripple effect on your entire system setup.
All devices on a network must have a unique IP Address
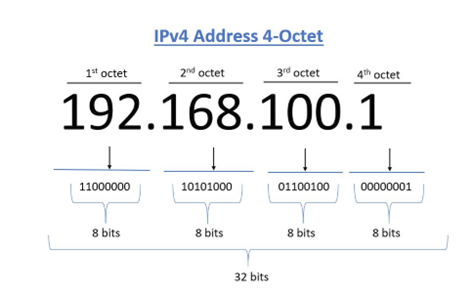
An IPv4 Address is a set of 4 octets, which is represented by a set of four numbers with a “.” in between each octet
The number is referred to as an Octet because it is a set of eight binary bits of information, that allow us to create a number from 0-255 (256 numbers, which is what 8 bits are capable of creating),
Subnet Masks
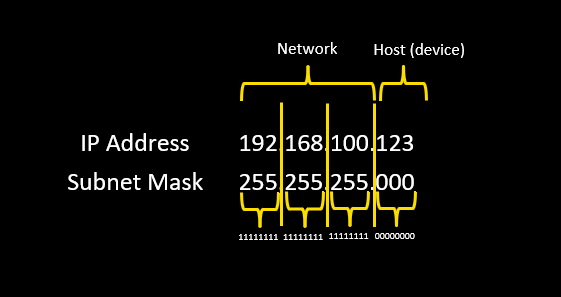
Subnet Masks determine whether one device can see another if they are on the same network
If the Network Octet (portion) of an IP address with associated subnet 255 in the same Octet matches another IP address, then those two devices will see each other
How to change Static IP and Subnet Mast
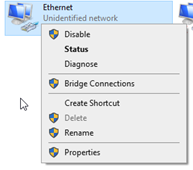
Right click on icon in Windows bar and select “Network and Internet Settings”

Select “Change Adapter Options”
Right click on a NIC (Network Interface Controller) and select properties
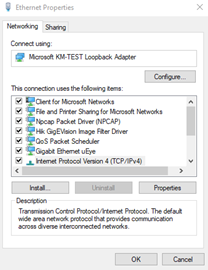
Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), then Properties again
Input IP address and Subnet Mask
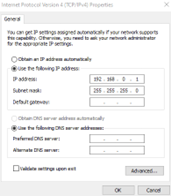
You can also access the Adapters by Pressing Windows+R to open the Run dialog box and typing in “ncpa.cpl”
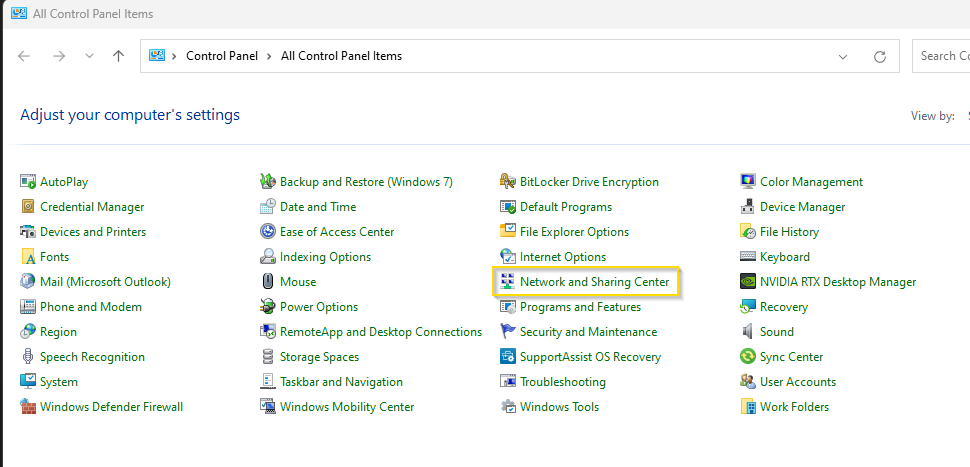
Additional you can navigate to the “Control Panel and select ”Network and Sharing Center":
Then “Change Adapter settings”: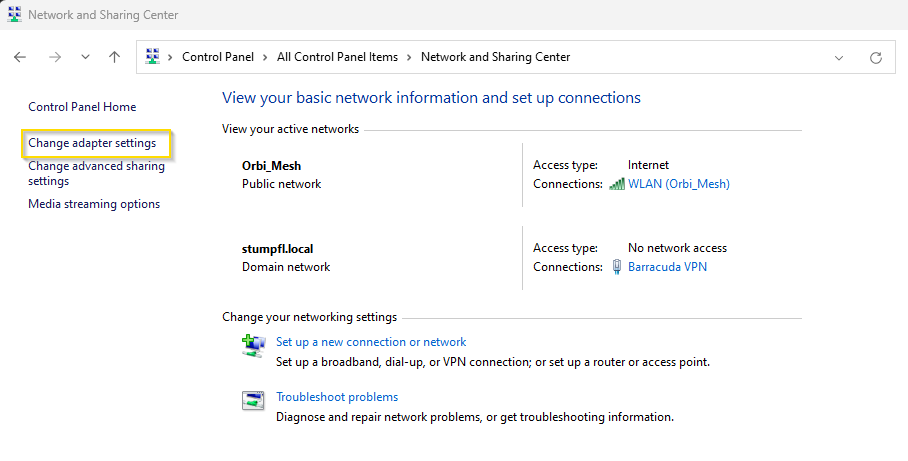
Afterwards follow the description as seen above.
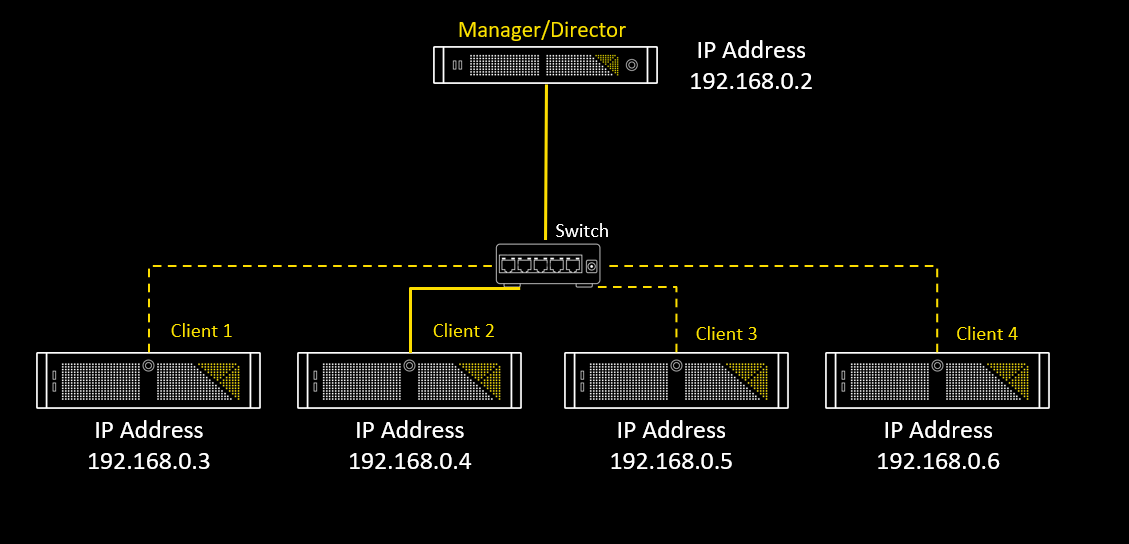
Unicast
One device sending to single destination device:
Broadcast
One device sending to all destination devices on the network, basically like yelling to everything on the network
Multicast
One device sending to multiple, specified devices simultaneously

 Contact Us
Contact Us


